Spring源码分析:IoC
In this post, we are going to diving into the Spring framework in deep. The main content of this post is to analyze IoC implementation in the source code of the Spring framework.
Basics
Basic Concepts
Bean and BeanDefinition
In Spring, the objects that form the backbone of your application and that are managed by the Spring IoC container are called beans. A bean is an object that is instantiated, assembled, and otherwise managed by a Spring IoC container.
A Spring IoC container manages one or more beans. These beans are created with the configuration metadata that you supply to the container, for example, in the form of XML <bean/> definitions.
Within the container itself, these bean definitions are represented as BeanDefinition objects.
BeanWrapper
BeanWrapper is the central interface of Spring’s low-level JavaBeans infrastructure. Typically not used directly but ranther implicitly via a BeanFactory or a DataBinder. It provides operations to analyze and manipulate standard JavaBeans: get and set property values, get property descriptors, and query the readability/writability of properties.
IoC Containers
IoC container is the implementation of IoC functionality in the Spring framework. The interface org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextrepresents the Spring IoC container and is responsible for instantiating, configuring, and assembling the aforementioned beans. The container gets its instructions on what objects to instantiate, configure, and assemble by reading configuration metadata. The configuration metadata is represented in XML, Java annotations, or Java code. It allows you to express the objects that compose your application and the rich interdependencies between such objects.
Several implementations of the ApplicationContext interface are supplied out-of-the-box with Spring. In standalone applications it is common to create an instance of ClassPathXmlApplicationContext or FileSystemXmlApplicationContext.
BeanFactory vs ApplicationContext
Spring provides two kinds of IoC container, one is XMLBeanFactory and other is ApplicationContext. The ApplicationContext is a more powerful IoC container than BeanFactory.
Bean Factory
- Bean instantiation/wiring
Application Context
- Bean instantiation/wiring
- Automatic BeanPostProcessor registration
- Automatic BeanFactoryPostProcessor registration
- Convenient MessageSource access (for i18n)
- ApplicationEvent publication
WebApplicationContext vs ApplicationContext
WebApplicationContext interface provides configuration for a web application. This is read-only while the application is running, but may be reloaded if the implementation supports this.
WebApplcationContext extends ApplicationContext. This interface adds a getServletContext() method to the generic ApplicationContext interface, and defines a well-known application attribute name that the root context must be bound to in the bootstrap process.
WebApplicationContext in Spring is web aware ApplicationContext i.e it has Servlet Context information. In single web application there can be multiple WebApplicationContext. That means each DispatcherServlet associated with single WebApplicationContext.
Class Hierarchy
Bean Factories Hierarchy
I-BeanFactory |
ApplicationContext Hierarchy
I-ListableBeanFactory |
AbstractApplicationContext Hierarchy
A-AbstractApplicationContext |
BeanRegister & BeanFactory Hierarchy
I-SingletonBeanRegistry |
DispatherServlet Hierarchy
A-javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet |
The Process of IoC Implementation
The following figure shows the process of IoC implementation.
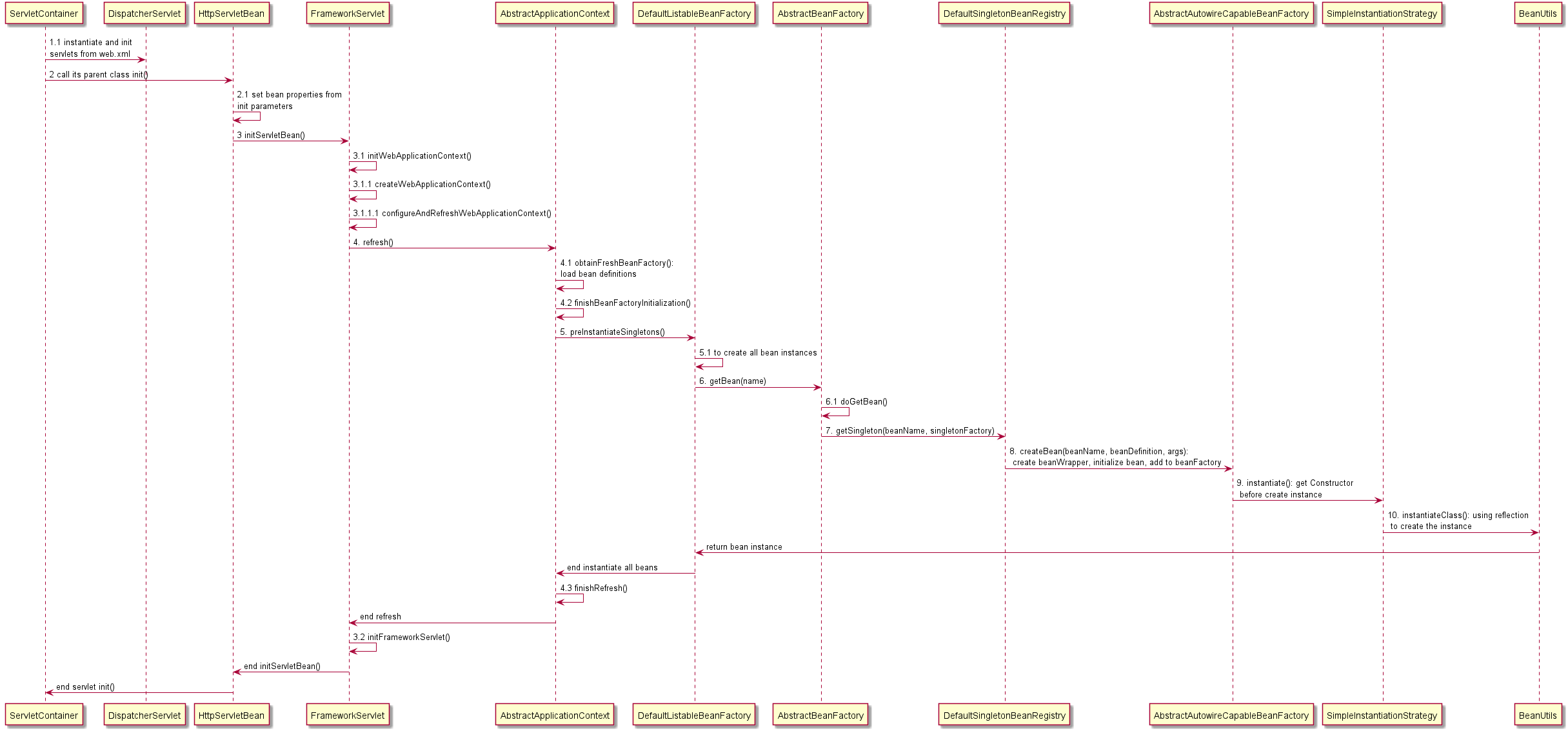
Next, We are going to analyze the implementation in the source code of every step.
1 Java web project starting
1.1 instantiate and init servlets from web.xml
When a Java web project running in an application server like Apache Tomcat, the servlet container of the server will load, instantiate, and init Java servlets that be <load-on-startup> from web.xml file.
<servlet> |
2 The DispatcherServlet initialization and Calling init() in HttpServletBean
2.1 set bean properties from init parameters
Set initial parameters specified in the web.xml file for the servlet instance DispatcherServlet.
3 initServletBean() in FrameworkServlet
3.1 initWebApplicationContext()
Initialize and publish the WebApplicationContext for this servlet.
- Check is there any WebApplicationContext instance or root application context, if not create a new webApplicationContext instance (See #3.1.1).
3.1.1 createWebApplicationContext()
Using reflection to create a WebApplicationContext instance, and configure it (see #3.1.1.1).
FrameworkServlet.java
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext( ApplicationContext parent) { |
3.1.1.1 configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext()
Set WebApplication instance properties and go to refresh (See #4).
FrameworkServlet.java
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac) { |
4 refresh() in AbstractApplicationContext
As this is a startup method, it should destroy already created singletons if it fails, to avoid dangling resources. In other words, after invocation of that method, either all or no singletons at all should be instantiated.
AbstractApplicationContext.java
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { |
4.1 obtainFreshBeanFactory()
Create a BeanFactory instance in AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext.
AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext.java
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException { |
4.2 finishBeanFactoryInitialization()
Initializate beanFactory, and go to instantiate bean instances (see #5).
AbstractApplicationContext.java
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { |
5 preInstantiateSingletons() in DefaultListableBeanFactory
Using Iterator of beanNames to get bean instances.
5.1 to create all bean instances
AbstractApplicationContext.java
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException { |
6 getBean(name) in AbstractBeanFactory
To get the bean instances.
AbstractBeanFactory.java
public Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException { |
6.1 doGetBean()
To get the bean instance by bean name.
AbstractBeanFactory.java
protected <T> T doGetBean(String name, Class<T> requiredType, Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly) throws BeansException { |
7 getSingleton(beanName, singletonFactory) in DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry
To get singleton bean instance.
DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.java
public Object getSingleton(String beanName, ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory) { |
8 createBean(beanName, beanDefinition, args) in AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
To get a bean instance, create a beanWrapper, initialize the bean, add add the bean to the beanFactory.
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java
protected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Object[] args) throws BeanCreationException { |
9 instantiate() in SimpleInstantiationStrategy
Get the Constructor of the bean class and to get the bean instance.
SimpleInstantiationStrategy.java
public Object instantiate(RootBeanDefinition bd, String beanName, BeanFactory owner) { |
10 instantiateClass() in BeanUtils
Using reflection to create a instance.
BeanUtils.java
public static <T> T instantiateClass(Constructor<T> ctor, Object... args) throws BeanInstantiationException { |
Conclusion
Spring framework uses the servlet container loads the DispatcherServlet when server startup to trigger the automatic beans instantiation.
The ApplicationContext is responsible for the whole process of beans instantiation. There is a BeanFactory as a field in the ApplicationContext, it is responsible to create bean instances.
The important steps of beans instantiation are: load bean definitions, create and initialize beanFactory, create and initialize bean instances, keep bean records in beanFactory.
References
[1] Spring Framework Source Code
[2] Spring Framework API - Current 5.2.7.RELEASE
[3] Spring Framework Documentation - 5.2.7.RELEASE
[5] Difference between ApplicationContext and WebApplicationContext in Spring MVC
[6] Spring life-cycle when we refresh the application context - Stack Overflow